Swine
Home
·
Disease
·
Swine
In mainly from four to 14 weeks of weaner, weight loss, general weakness, respiratory distress, diarrhea, pale skin or such as jaundice, representing infection with a variety of debilitating disease as a mortality rate (0-50%) to show.
1. Agent
: Porcine Circovirus type2 (PCV-2)
PCV2 infection alone does not matter, other agents ( Virus: PRRSV, PPV
, Bacteria: Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae,
Strepococcus suis, Pasteurella multocida,
Haemophilus parasuis, etc.) mixed infection appeared the symptoms.
The PCV-2 not mean that the infection PMWS,
Clinical symptoms and pathological findings, the detection of PCV-2, three conditions must be met for this.
2. Epidemiology
① Found in 1991 in Canada, in North America, Europe, Japan, China, Korea and all over the world occurred
② once outbreak lasted for several months
③ early weaning, crowdy, poor ventilation, excessive vaccinations cause PMWS
3. Transmission
① initial PMWS
- Maternal antibody falling period of 5-8 weeks (rare infection in piglets suckling)
- Show the typical PMWS (runt, abdominal breathing, diarrhea) symptoms
- Complications: Glasser's disease, mycoplasma, streptococcus, E. coli,
② mid-term PMWS
- PMWS domestic type
- Onset: 8 weeks to 13 weeks of age
- Mortality is high with runt accompanied by diarrhea (over 40%).
- Complications: salmonellosis, colitis
③ the end of PRDC
- Grower and Finisher in pigs (15 weeks to 20 weeks)
- Runt associated with chronic respiratory disease
- Complications: PRRS, Mycoplasma
4. Clinical Signs
① chronic runt and weight loss, emaciated, pale skin
② Respiratory System : dyspnea, cough, pneumonia
③ Digestive System : diarrhea
④ rare symptoms: jaundice, neurological symptoms, cyanosis, sudden death
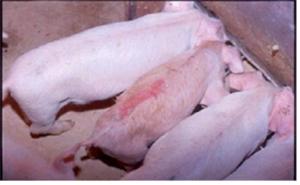
5. Gross Pathological Findings
① spleen and systemic lymph nodes enlargement
② respiratory system : chronic pneumonia, spots, interstitial pneumonitis
③ Digestive System : gastric ulcer
④ urinary system: renal pallor, edema, milky white (sulfur) circular spots appear when cutting
⑤ lymph nodes: enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes
< Histopathological Findings >
① lymph nodes : lymphocyte loss, lymphocytic, histiocytic or granulomatous inflammation
② lungs, liver, kidneys, pancreas and ileum t: lymphocytic, histiocytic or granulomatous inflammation
6. Diagnosis
① IFA (Indirect fluorescence antibody test, fluorescent antibody test), IHC
(Immunohistochemistry), genetic testing (PCR), serology and virus isolation tests
② Differential Diagnosis: Glasser's disease, PRRS
7. Prevention
① reduced stocking density, all-in all-out strict breeding
② prohibit other inlet pig farms and mixed breed, ban mixed age breeding pigs and other
③ avoid causing environmental stress
④ washed and disinfected thoroughly
⑤ vaccine for immunization and respiratory diseases, so thoroughly mixed infections when damage is increased
⑥ isolation of infected pigs by early diagnosis and rapid culling
⑦ secondary infection prevention and regular circo vaccination
1. Agent
: Porcine Circovirus type2 (PCV-2)
PCV2 infection alone does not matter, other agents ( Virus: PRRSV, PPV
, Bacteria: Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae,
Strepococcus suis, Pasteurella multocida,
Haemophilus parasuis, etc.) mixed infection appeared the symptoms.
The PCV-2 not mean that the infection PMWS,
Clinical symptoms and pathological findings, the detection of PCV-2, three conditions must be met for this.
2. Epidemiology
① Found in 1991 in Canada, in North America, Europe, Japan, China, Korea and all over the world occurred
② once outbreak lasted for several months
③ early weaning, crowdy, poor ventilation, excessive vaccinations cause PMWS
3. Transmission
① initial PMWS
- Maternal antibody falling period of 5-8 weeks (rare infection in piglets suckling)
- Show the typical PMWS (runt, abdominal breathing, diarrhea) symptoms
- Complications: Glasser's disease, mycoplasma, streptococcus, E. coli,
② mid-term PMWS
- PMWS domestic type
- Onset: 8 weeks to 13 weeks of age
- Mortality is high with runt accompanied by diarrhea (over 40%).
- Complications: salmonellosis, colitis
③ the end of PRDC
- Grower and Finisher in pigs (15 weeks to 20 weeks)
- Runt associated with chronic respiratory disease
- Complications: PRRS, Mycoplasma
4. Clinical Signs
① chronic runt and weight loss, emaciated, pale skin
② Respiratory System : dyspnea, cough, pneumonia
③ Digestive System : diarrhea
④ rare symptoms: jaundice, neurological symptoms, cyanosis, sudden death

5. Gross Pathological Findings
① spleen and systemic lymph nodes enlargement
② respiratory system : chronic pneumonia, spots, interstitial pneumonitis
③ Digestive System : gastric ulcer
④ urinary system: renal pallor, edema, milky white (sulfur) circular spots appear when cutting
⑤ lymph nodes: enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes
< Histopathological Findings >
① lymph nodes : lymphocyte loss, lymphocytic, histiocytic or granulomatous inflammation
② lungs, liver, kidneys, pancreas and ileum t: lymphocytic, histiocytic or granulomatous inflammation
6. Diagnosis
① IFA (Indirect fluorescence antibody test, fluorescent antibody test), IHC
(Immunohistochemistry), genetic testing (PCR), serology and virus isolation tests
② Differential Diagnosis: Glasser's disease, PRRS
7. Prevention
① reduced stocking density, all-in all-out strict breeding
② prohibit other inlet pig farms and mixed breed, ban mixed age breeding pigs and other
③ avoid causing environmental stress
④ washed and disinfected thoroughly
⑤ vaccine for immunization and respiratory diseases, so thoroughly mixed infections when damage is increased
⑥ isolation of infected pigs by early diagnosis and rapid culling
⑦ secondary infection prevention and regular circo vaccination